
RESEARCH PROJECT
Multimodal intuitive no-code robot teaching
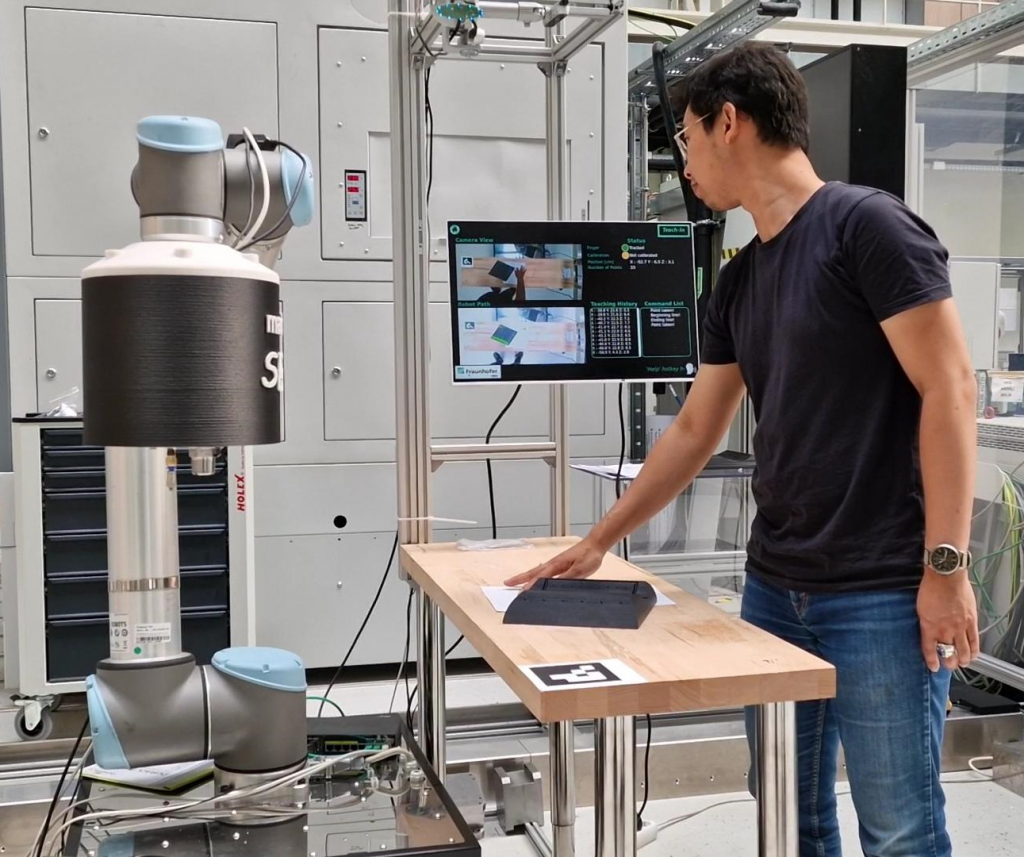
Robotic programming requires domain- and platform-specific know-how which is inacessible for non-expert users. To be able to adapt in versatile and agile production concept, robotic programming should be implemented with low- or no-code approach. In my research at Fraunhofer IWU, I had developed a novel approach for robotic teaching by combining speech and hand-/finger-gesture. The system can be implementible and integrible with diverse sensor and robot systems due to its hardware agnostic approach and generic data structure.
The hand or finger movements will be tracked markerless-ly using computer vision-based algorithms. Hence, the generalized movement coordinates is transformed into specific robot programming language. The speech recognition system allows the user to interact naturally with the system. The assessment and benchmarking in the system depict that such approach can reduce programming effort and time up to 30x and the precision of the system benchmarked with a low-cost RGB-D camera delivers 6 mm accuracy. By implementing process oriented AI and CV functionalitites, the precision can be increased in performing specific industrial tasks, such as welding, and deburring.
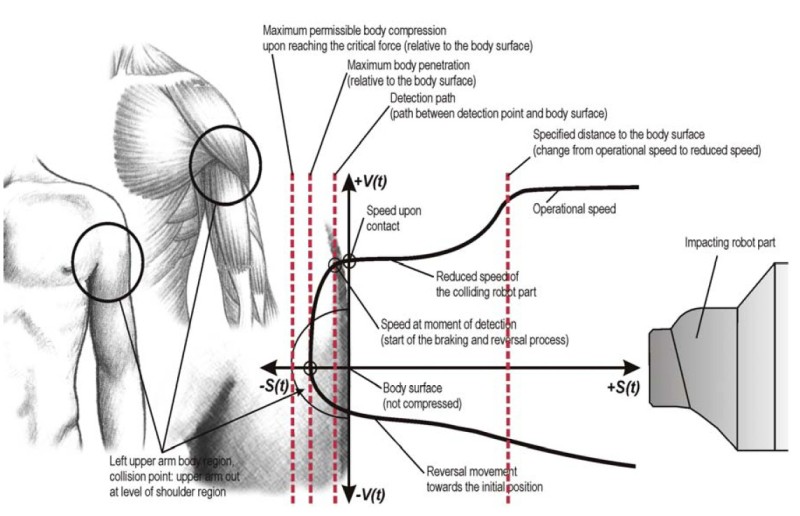
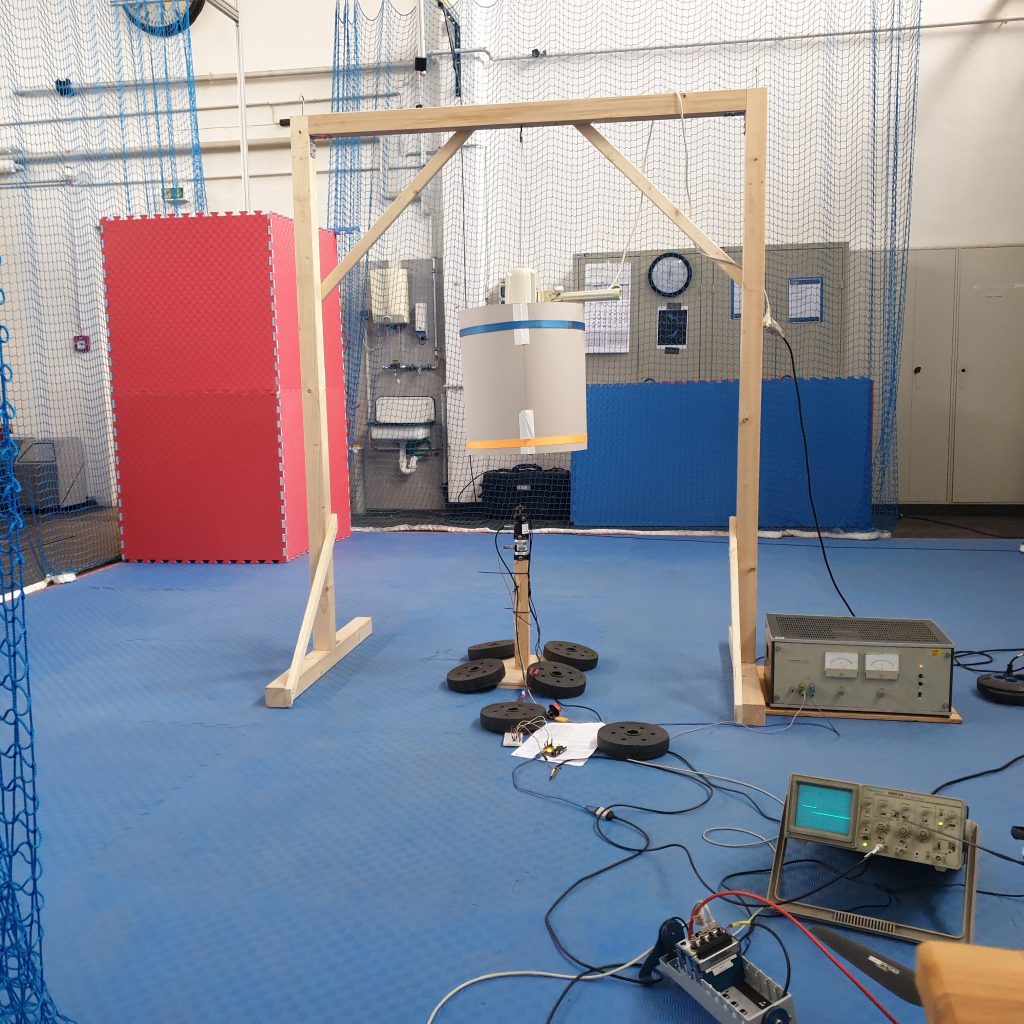
Human-robot collision model
In a collaborative robotic system, collisions could occur under biomechanical limits (ISO / TS 15066). The collisions between robotic systems and humans can lead to serious injuries. From the state-of-the-art, collision assessment must be performed by measuring force torque and performing validation for the related force-torque sensors. This approach is complex, tedious, and in some cases not practicable. From this point of view, a mathematical model for human-robot collision will assist the end-users in parametrizing the robot systems to achieve collision-conformed states. I have worked on developing the collision model between humans and robots in collaboration cases.
Thrust control via wrench observer
Simplification in modelling a thrust in multicopter rotor leads to instability in controlling the multicopter body when disturbances occur. In the state-of-the-ar, the thrust force in the drone control system is modeled by a product of thrust coefficient with a quadratic of motor RPM. Hence, drone stability can not be guaranteed if external disturbance forces occur on the rotor. In this work, a wrench observer is built based on the mathematical/physical model from the power conservation law. The observation is implemented using current, voltage, and RPM of the rotor. In this case, the aerodynamical power modeling must be equal to the mechanical and the electrical power modeling. By observing the wrench, the new thrust coefficient can be calculated newly based on the actual state of the rotor influenced by the external disturbances.
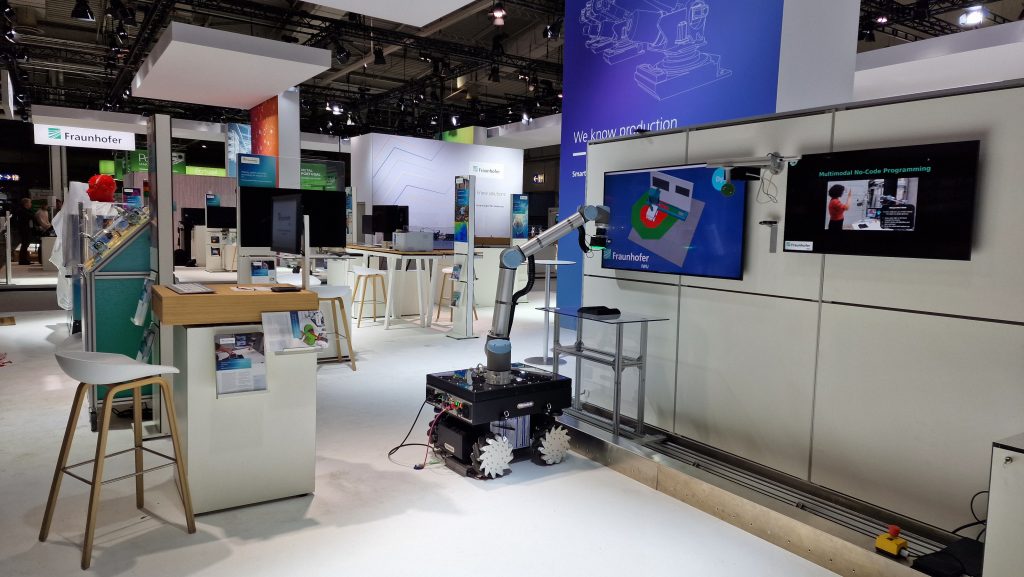


Industrial human-robot collaboration
My research focus in Fraunhofer IWU is based on the field of human-robot collaboration. This covers the development of robotics control system algorithms, sensor-data processing, computer vision, development of mechatronic system, risk assessment, and also functional safety.
Publication
Pasadena, USA, 2024
IEEE ROMAN 2024
Halim, Jayanto, Eichler, Paul, Krusche, Sebastian, Mohamad Bdiwi, and Steffen Ihlenfeldt. “A Hybrid Approach of No-Code Robot Programming for Agile Production: Integrating Finger-Gesture and Point-Cloud.” In 2024 33rd IEEE International Conference on Robot and Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN). IEEE.
Chemnitz, Germany, 2024
IEEE ROSE 2024
Halim, Jayanto, Mohamad Bdiwi, and Steffen Ihlenfeldt. “A No-Code Approach for Intuitive Robot Programming for Agile Welding Application.” 2024 IEEE International Symposium on Robotic and Sensors Environments (ROSE). IEEE, 2024.
Dubai, UAE, 2023
IEEE ICAR 2023
Al Naser, I., Halim, J., Bauer, S., Gönültas, D., Bdiwi, M., & Ihlenfeldt, S. (2023, December). An Approach for Dynamic Robot-Risk Assessment in Agile Manufacturing Process towards Industry 4.0. In 2023 21st International Conference on Advanced Robotics (ICAR) (pp. 355-360). IEEE.
Busan, South Korea, 2023
IEEE ROMAN 2023
Halim, J., Eichler, P., Krusche, S., Bdiwi, M., & Ihlenfeldt, S. (2023, August). Enhanced No-Code Finger-Gesture-Based Robot Programming: Simultaneous Path and Contour Awareness for Orientation Estimation. In 2023 32nd IEEE International Conference on Robot and Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN) (pp. 1502-1508). IEEE.
Dubai, UAE, 2022
IEEE ROSE 2022
Bdiwi, M., Krusche, S., Halim, J., & Ihlenfeldt, S. (2022, November). Superordinate Safety System for Human Robot Interaction in Complex Industrial Environment. In 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Robotic and Sensors Environments (ROSE) (pp. 1-7). IEEE.
Bdiwi, M., Krusche, S., Halim, J., Eichler, P., Hou, S., Rashid, A., … & Ihlenfeldt, S. (2022, November). Situational zone-based robot control for heterogeneous safety sensors in agile HRI applications. In 2022 IEEE International Symposium on Robotic and Sensors Environments (ROSE) (pp. 01-07). IEEE.
2022
Frontiers in Robotics and AI
Halim, J., Eichler, P., Krusche, S., Bdiwi, M., & Ihlenfeldt, S. (2022). No-code robotic programming for agile production: A new markerless-approach for multimodal natural interaction in a human-robot collaboration context. Frontiers in Robotics and AI, 9, 1001955.
Bdiwi, M., Al Naser, I., Halim, J., Bauer, S., Eichler, P., & Ihlenfeldt, S. (2022). Towards safety4. 0: A novel approach for flexible human-robot-interaction based on safety-related dynamic finite-state machine with multilayer operation modes. Frontiers in Robotics and AI, 9, 1002226.
Vancouver, Canada, 2021
IEEE ROMAN 2021
Eichler, P., Rashid, A., Al Nasser, I., Halim, J., & Bdiwi, M. (2021, August). Modular System Design Approach for Online Ergonomics Assessment in Agile Production Environment. In 2021 30th IEEE International Conference on Robot & Human Interactive Communication (RO-MAN) (pp. 1003-1010). IEEE.
ORCID:
Proudly powered by WordPress
